When I upgraded to Windows 11, I wanted to explore virtualization options to run other operating systems and experiment with software. After researching various virtual machines (VMs), I discovered that there are several tools that can help create and manage virtual machines on a Windows 11 system. In this article, I will explain the main options: Hyper-V, VMware, and VirtualBox. I will also discuss which one might be the best choice depending on your needs.
Virtual Machines for Windows 11
With Windows 11, running virtual machines is a straightforward process, but it depends on choosing the right VM software. A virtual machine allows you to create an isolated environment where you can run a completely different operating system or multiple operating systems on the same hardware. For instance, you could run Linux or older versions of Windows inside a VM while still using Windows 11 as your primary operating system.

Let’s look at the most popular virtual machine software options available for Windows 11: Hyper-V, VMware, and VirtualBox.
Hyper-V: Built-In Virtual Machine Software for Windows 11
Hyper-V is Microsoft’s native virtualization platform, and it is available on Windows 11 Pro, Enterprise, and Education editions. One of the biggest advantages of Hyper-V is that it is integrated into the operating system, making it highly compatible with Windows 11. Since it’s a Microsoft product, it tends to work well without any additional setup or compatibility issues.
Pros of Hyper-V:
- Performance: Since Hyper-V is built directly into Windows 11, it offers excellent performance and seamless integration with the system’s resources.
- Security: Hyper-V provides robust security features, such as isolation of virtual machines, which helps keep your primary system safe from vulnerabilities.
- No Additional Software Required: As Hyper-V is part of Windows 11, you don’t need to install any extra software if you’re using the Pro version or higher.
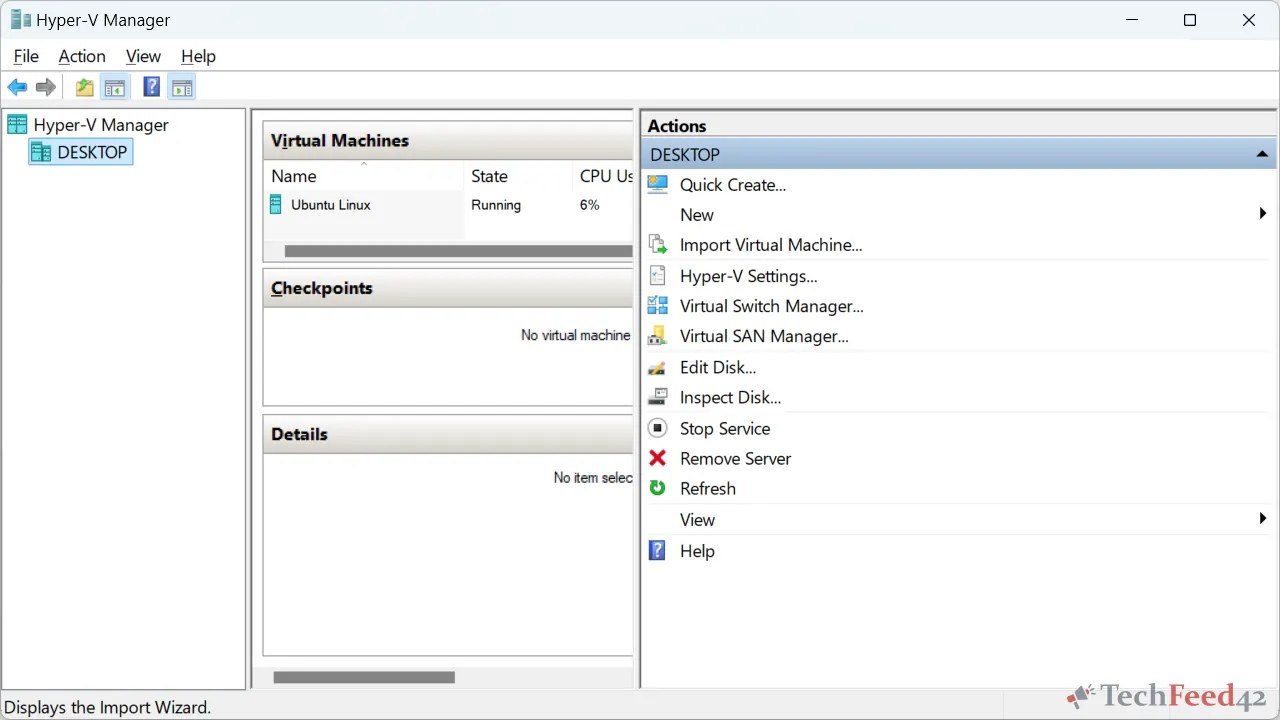
Cons of Hyper-V:
- Not Available on Windows 11 Home: If you are using the Home edition of Windows 11, Hyper-V isn’t included, so you’ll need to upgrade or look for another option.
- Limited to Windows Users: Hyper-V is more focused on running Windows virtual machines and is less flexible when it comes to running other operating systems like macOS.
VMware Workstation: A Powerful Virtual Machine Option
VMware Workstation is another popular virtualization tool that works well with Windows 11. It’s known for its user-friendly interface and solid performance. VMware has been around for years and is widely trusted in the virtualization space.
Pros of VMware:
- Compatibility with Multiple Operating Systems: VMware is versatile and can run a wide range of guest operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS.
- Easy to Use: VMware Workstation is one of the simplest virtual machine solutions out there. The interface is intuitive, even for beginners, making it easy to set up and manage virtual machines.
- Snapshot Feature: VMware lets you take snapshots of virtual machines, which is very useful if you want to create restore points or go back to a previous state after making changes.
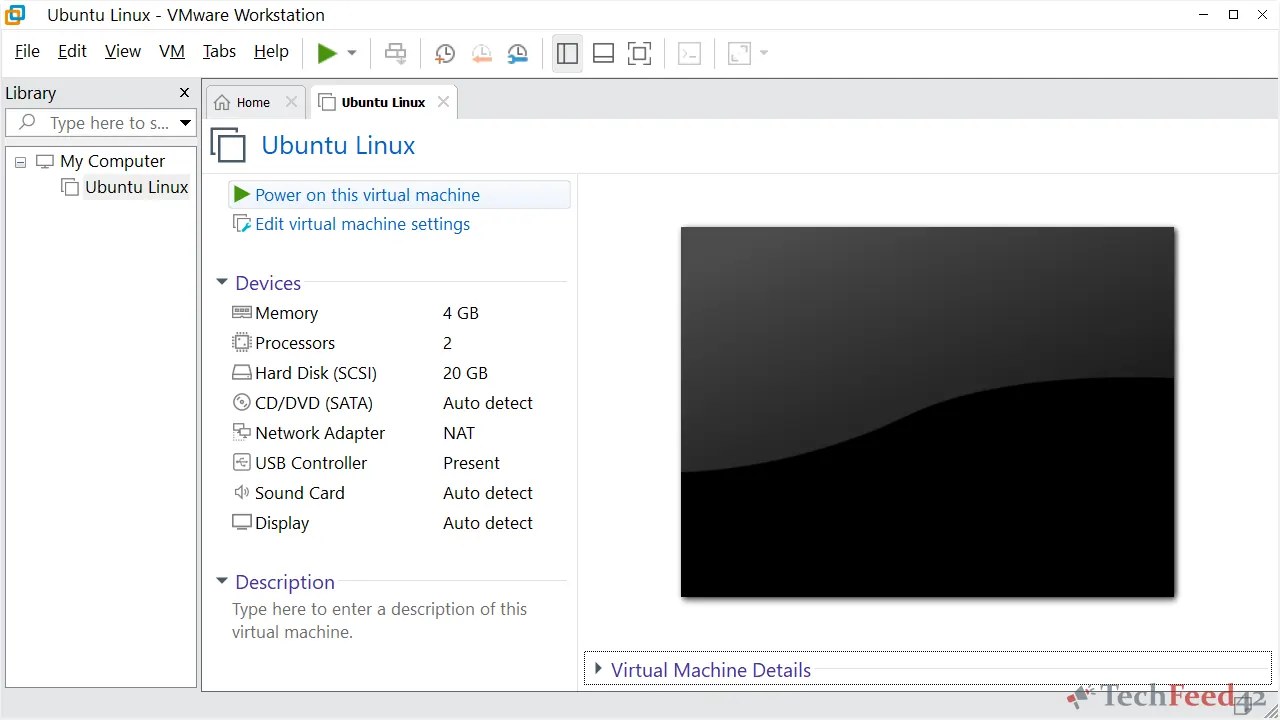
Cons of VMware:
- Paid Features: While VMware Workstation is free for personal use, it lacks some advanced features like cloning and linked clones, which are available in the paid VMware Workstation Pro.
- Resource Intensive: VMware tends to be more demanding on system resources compared to Hyper-V, so it might not be the best option if you are working with limited hardware.
VirtualBox: The Free and Open-Source Option
VirtualBox is a popular free and open-source virtualization tool that works on Windows 11. It is known for being lightweight, flexible, and highly compatible with different operating systems. One of the key attractions of VirtualBox is that it’s completely free to use for personal and professional purposes.
Pros of VirtualBox:
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: VirtualBox runs on a variety of host operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS, making it versatile for users who need to switch between different platforms.
- Free to Use: As an open-source project, VirtualBox is entirely free, making it the ideal choice for those who need virtualization on a budget.
- Support for Different Guest Systems: Like VMware, VirtualBox supports a wide range of guest operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and others.
Cons of VirtualBox:
- Performance Issues: VirtualBox might not be as fast or efficient as Hyper-V or VMware, especially when running resource-intensive applications.
- Complex Setup for Certain Features: While VirtualBox is user-friendly for basic virtualization tasks, some advanced features like USB device support or shared folders require additional setup.
Which Virtual Machine Is the Best Choice?
When deciding which virtual machine software is the best for Windows 11, it ultimately depends on your needs and the system you’re using.
- If you’re running Windows 11 Pro or higher and want a fast, reliable VM with minimal setup, Hyper-V is an excellent choice. It’s built into the system, so it integrates well with Windows, but it’s not available for Home users.
- If you need a more versatile solution that supports a wide range of operating systems and don’t mind paying for extra features, VMware Workstation is a great option. Its ease of use and strong performance make it a popular choice for both beginners and professionals.
- If you’re looking for a free virtualization tool and don’t mind sacrificing a bit of performance, VirtualBox offers the most flexibility, especially if you want to experiment with multiple operating systems.
For me, the best option turned out to be Hyper-V because I’m using Windows 11 Pro, and I needed something that was fast and integrated into my system. However, if I were using Windows 11 Home, I might have leaned towards VMware or VirtualBox, depending on my budget and needs.
In conclusion, choosing the right virtual machine software for Windows 11 involves considering your specific requirements, system resources, and what you need to achieve. Each option – Hyper-V, VMware, and VirtualBox – has its own strengths and weaknesses, so evaluating them carefully will help you make the best choice.